Who Has to File TDS Returns?
The main concept of TDS came into existence with the objective of collecting tax from the source of income. You must file an income tax return whether your employer withheld tax at source (TDS) from your pay or you paid tax yourself (ITR). This is due to the fact that TDS and income tax are computed and paid in distinct ways.
According to this idea, a person (the deductor) who is required to make a payment of a certain sort to another person (the deductee) must withhold tax at source and send it to the Central Government. On the basis of Form 26AS or a TDS certificate provided by the deductor, the deductee from whose income tax source deductions have been made is entitled to get credit for the amount so deducted.
What is TDS?
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) can be defined as a specific amount that is deducted during certain transactions such as salary, commission, rent, interest, professional fees, etc. This amount is deposited to the Income Tax Department by the deductor on behalf of the tax payer. In this instance, the tax must be subtracted at the moment the funds are credited to the payee’s account or, if earlier, at the time of payment. The tax is typically subtracted between 10% and 15%.
What is TDS Return?
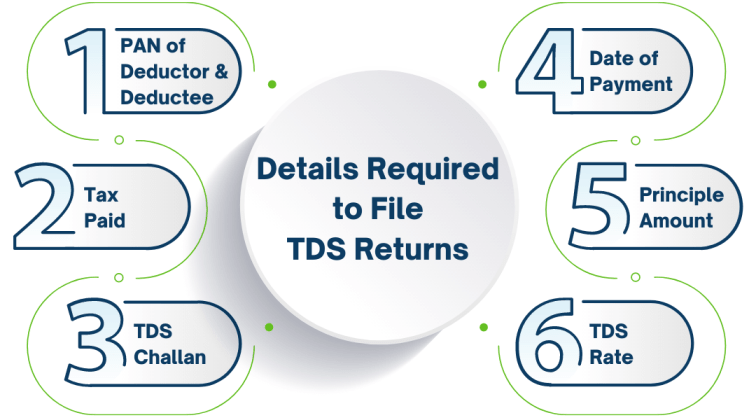
The ideal way to define a TDS return is as a statement or a summary of all TDS-related transactions that took place within a given quarter. Usually, it contains information on the TDS that the deductor has collected and submitted to the Income Tax Authority. The crucial information shown in a TDS return statement consists of the following:
- Deductor and deductee’s PAN.
- Challan details
- Particulars of TDS paid
Notably, the payee’s Form 26AS includes all the information that is revealed in the online TDS return form. All those who fall within the jurisdiction of the tax slabs set forth by the IT department must comply.
Usually, those who qualify can submit their TDS returns online using the IT department’s e-filing system. One must pay a minimum fine of Rs. 100,000 for postponing the procedure if they fail to file TDS returns within a year of the due date.
The penalty must also be paid if inaccurate information is provided. Notably, Section 234 mandates that taxpayers who fail to submit their TDS returns by the deadline shall pay a penalty of Rs. 200 each day till they are submitted. No matter what, the total obligation cannot at any time be greater than the TDS amount.
Who is Eligible for TDS Return?
Organizations and employers with valid TAN are eligible to file TDS returns. Each quarter, those whose accounts are audited in accordance with Section 44AB and who have a position of authority within organizations or the government needs to undergo TDS return filing.
This indicates that the deductor may be any of the following: an individual, a group of individuals, a HUF, a limited company, a local authority, a group of individuals forming an association, a partnership firm, etc.
TDS is submitted against the following pay-outs in accordance with ITA:
- Salary income
- Income on securities
- Insurance commission
- Pay-outs towards NSC
- Earnings generated on winning horse race
- Earnings are generated on winning a lottery, puzzles, etc.
Who is required to e-file TDS return?
The following deductors must compulsorily file their TDS Returns online:
- All Government Offices
- Every person whose accounts need auditing
- All companies
- Any other deductor if a return reflects 20 or more deductees for any quarter of the financial year.
What is the Rate of TDS Deduction?
TDS deductions must be made from income that is obtained from wages, professional fees, commissions, rent, interest earned, etc. The source of income and the overall amount of revenues produced determines the amount of TDS imposed on earnings.
In layman’s terms, various forms of income are subject to varying TDS rates. It should be emphasized that tax is paid on earnings in excess of the maximum threshold level. TDS rates often range from 1% to 30% and are highly influenced by the amount of income taxed.
What is a Revised TDS Return?
It should be noted that the tax amount deposited with the government will not appear in Form16/Form16A/Form26AS if an error, such as a mistake in the challan or PAN data, is found in the TDS return filing.
One must fix the mistakes by submitting a corrected TDS to prevent them. When filing the amended TDS returns, the following should be kept in mind:
- The Tax Information Network central system must approve the original return before sending a TDS Return.
- At the official website of NSDL, taxpayers may use their PAN and Provisional Receipt Number to verify the status of their TDS return.
- Using this modified TDS statement, taxpayers can create a revised TDS Return. A copy of this report is available for download from the TDS Reconciliation Analysis and Correction Enabling System, or TRACES, website.
Any business or person making the payment must deduct tax at source if payment exceeds the government-specified limit. Advantages of TDS Taxpayers and the government both benefit from filing returns. Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is the advance tax paid by any person or organization for making contact payments, interest payments, professional fee payments, salary payments, dividend payments, and other payments as per the government’s stipulated tax slabs on behalf of the payee. Read More from Wikipedia




